Teacher Explains
✨ Fundamental Rights
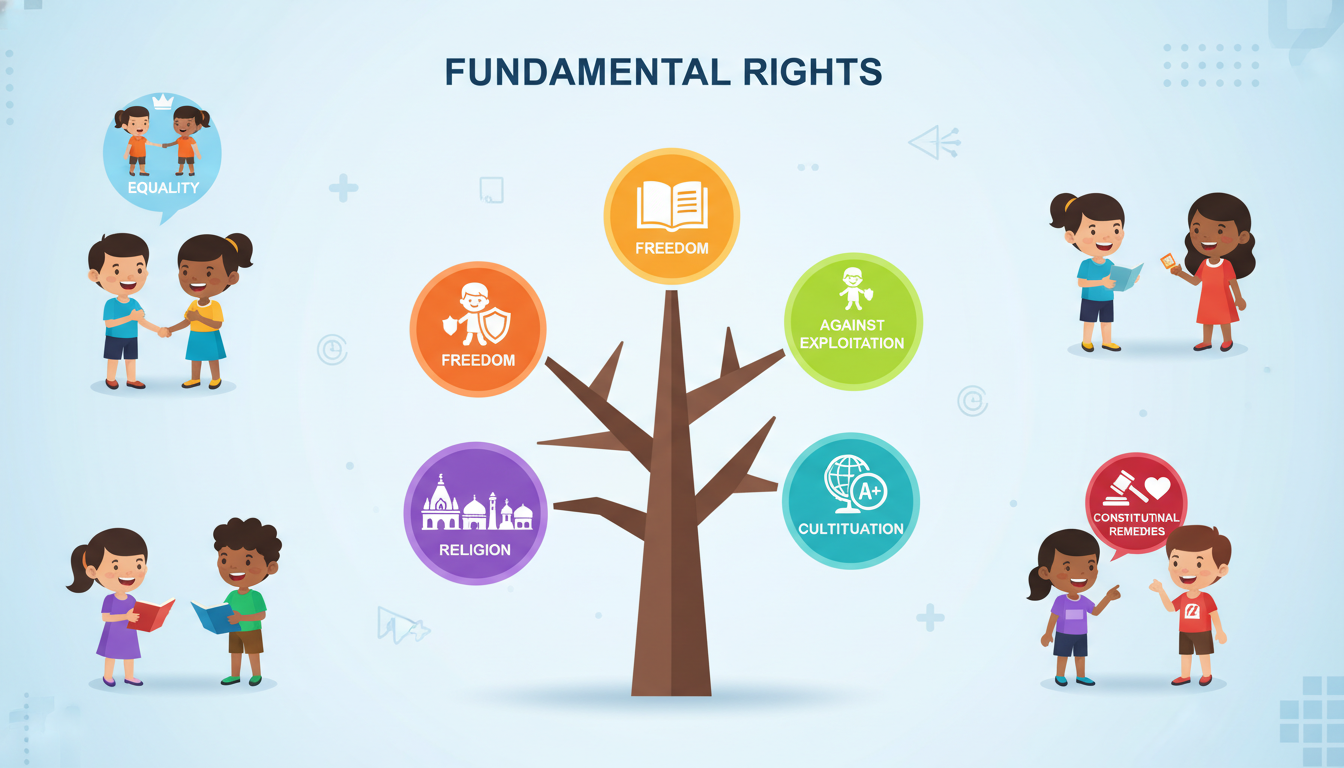
Okay class, let's explore how the Indian Constitution helps marginalized groups. Remember from our first chapter, the Constitution outlines the principles that make our society democratic. A key part of this is the list of Fundamental Rights, which are available to all Indians.
✨ Marginalized Groups' Use of Rights
Marginalized communities have used these rights in two important ways. First, by asserting their Fundamental Rights, they've pushed the government to acknowledge the injustices they face. Second, they've demanded that the government actively enforce these laws to protect them. Sometimes, these struggles have even led to new laws that better reflect the spirit of the Fundamental Rights.
✨ Article 17: Abolition of Untouchability

For example, Article 17 of the Constitution abolishes untouchability. This means that no one can stop Dalits from getting an education, entering temples, or using public facilities. It also declares that practicing untouchability is wrong and won't be tolerated. In fact, it's now a punishable crime!
✨ Article 15: Prohibition of Discrimination

Furthermore, Article 15 reinforces this by stating that no Indian citizen can be discriminated against based on religion, race, caste, sex, or place of birth. Dalits have used this article to fight for equality where it's been denied. These articles are powerful tools for marginalized communities seeking justice and equality.
